
Chaldean Numerology is an oldest numerological system developed by Chaldeans who once occupied Chaldea - a marshy land located in modern-day southern Iraq which came to rule Babylon briefly. When the Babylonian Empire was absorbed into the Persian Achaemenid Empire the name "Chaldean" lost its meaning as the name of a race of men, and came to be applied only to a social class. The Persians found the Chaldeans masters of reading and writing, and especially versed in all forms of incantation, in sorcery, witchcraft, and the magical arts. They quite naturally spoke of astrologists and astronomers as Chaldeans. It therefore resulted that Chaldean came to mean astrologist. In this sense it is used in the Book of Daniel (Dan. i. 4, ii. 2 et seq.), and with the same meaning it is used by the classical writers.
Chaldeans were analyzing both the name and the birth date of a person. They didn’t use an original name (written in the birth certificate) as Pythagoreans, but considered only the name the person is most known by.
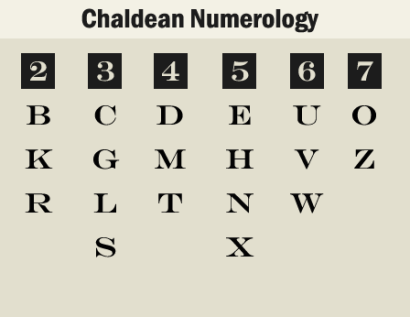
Chaldeans astrologers also had no number Nine (9) in their calculations and so, Chaldean numerological alphabet system differs from Pythagoreans.
Chaldeans believed in a sacred, holy qualities of number Nine (9), and hold it away from all other numbers. However, if your name is total 9, then the 9 remains.
But in this system it isn’t enough to know what the single number mean. One must also know the meaning of the “compound”, or “double” numbers. The single number simply represents the physical, outward appearance of a person’s name, whereas the compound number represents the deeper, metaphysical hidden influences of forces behind the name.
For example,
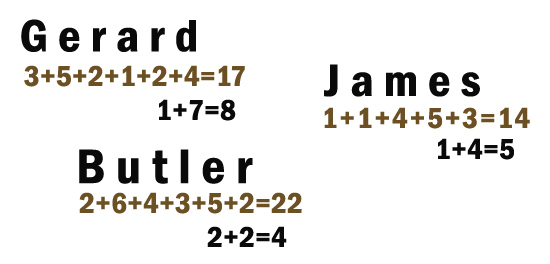
my name also
In God's will
That is me, totally and incredibly